LDAT stands for Landfill Degradation and Transport model. The modelling environment solves the LDAT constitutive equation whilst satisfying the initial and boundary conditions applied to the model. The constitutive equation is assembled from the well-known physical and bio-chemical relationships that represent the material changes caused by bio-chemical and physical processes that are taking place in the landfill. The modelling environment is a framework constructed from LDAT Elements. The LDAT Element is the object at the heart of any LDAT landfill model.
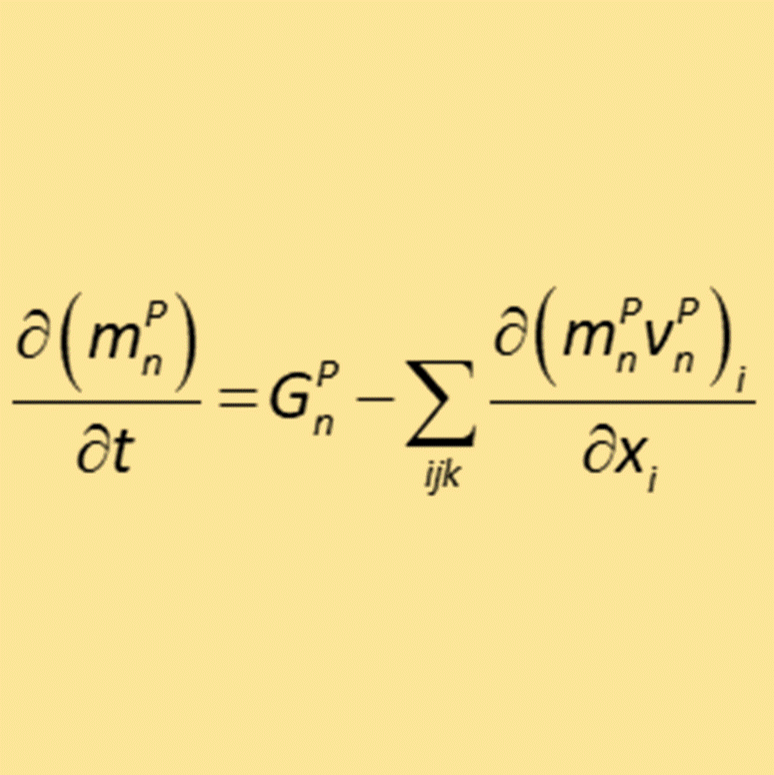
Landfill waste processes
The LDAT constitutive equation
LDAT model element
What is a waste landfill?
Our landfill waste degradation and transport model system is based on a group of analytically derived algebraic equations that together represent the physical and bio-chemical processes taking place in a waste landfill. The model produces the data required to simulate the behaviour of landfill waste. In terms of scale, the model simulation can be a representation of anything between a whole waste landfill and a large landfill waste sample.
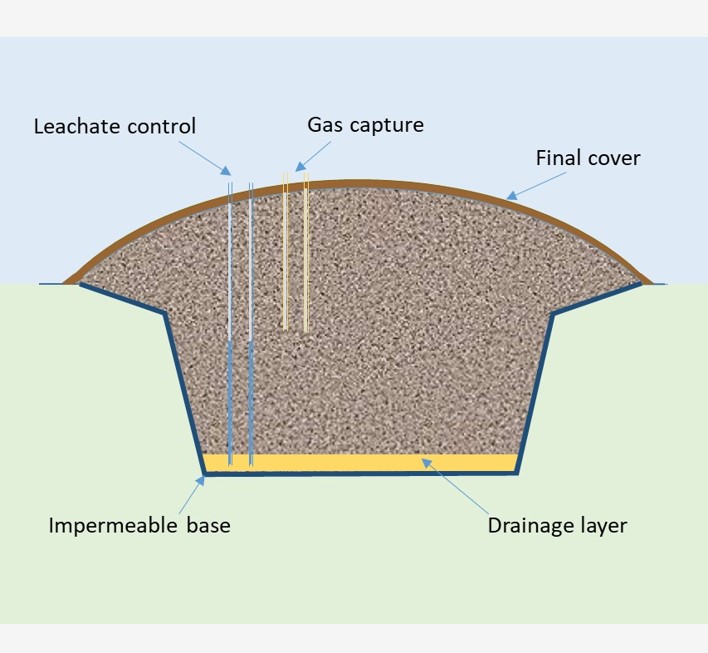
What is a waste landfill? A waste landfill is a hole in the ground that gets filled with the waste we produce after we can think of nothing else to do with it! Unfortunately it can emit gases and liquids that are a threat to human health and the natural environment. By simulating these problems using models like the LDAT landfill waste and transport model we can find out how to design and operate waste landfills safely. …MORE
What is a landfill waste?
What is a landfill waste? Everything we produce for ourselves and then consume (useful things like food, clothes, books, houses, furniture and so on) leaves behind something that we don’t want. And even when we try to reduce this unwanted production by reuse, recycling, or by conversion to energy, we are still left with something. So we put it in a landfill – and it becomes landfill waste. …MORE
The LDAT model calculation engine assembles the group of coupled process equations into a single constitutive equation. The calculator then solves this equation, whilst at the same time satisfying the initial and boundary conditions applied to the model. The unique constitutive equation takes the form of a standard unsaturated flow equation in which the impact of the non-flow landfill processes is bundled into the source term.
The constitutive equation takes the form of a multi-component multi-phase flow model. The source term of this equation is arranged to accommodate the landfill processes of dissolution, waste degradation, gas solubility, gas diffusion, chemical equilibrium, and the impact of temperature changes due to heat generation and transfer. The LDAT calculation engine solves the landfill process constitutive equation using a finite difference algorithm within a framework of rectangular representative elementary volumes. ...MORE
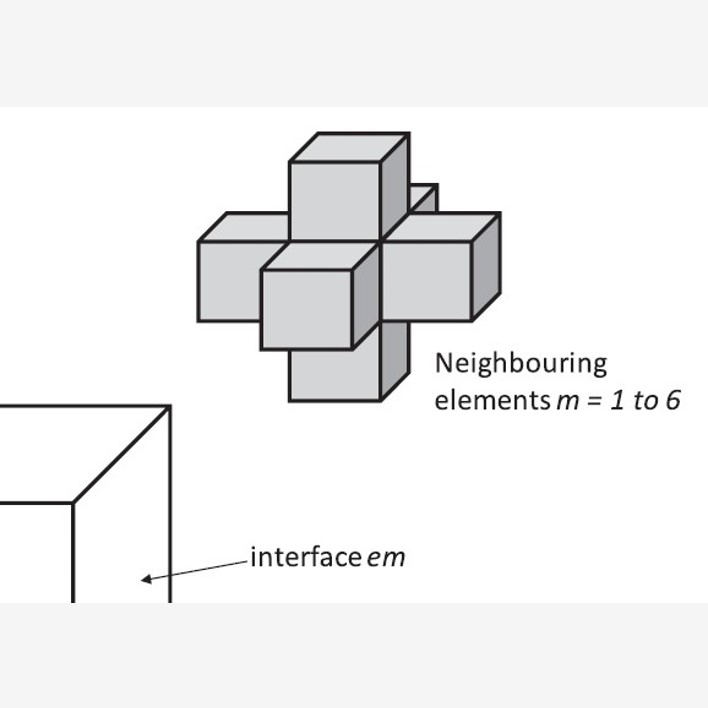
The LDAT model calculation engine operates on the LDAT model element. This element is a three dimensional rectangular representative space, that contains the values of all of the parameters required to define the state of material contained in the element space at any point in time.
A basic principle of the LDAT landfill modelling approach is that the state of the waste at any time is completely defined by, 1) the mass of all the chemical compounds contained in an element of the waste (in all of the solid, gas and liquid phases), and 2) the stresses applied to the element of waste in the form of total stress, temperature, and the gas and liquid pressures.